How to connect a TFT LCD display to the motherboard?
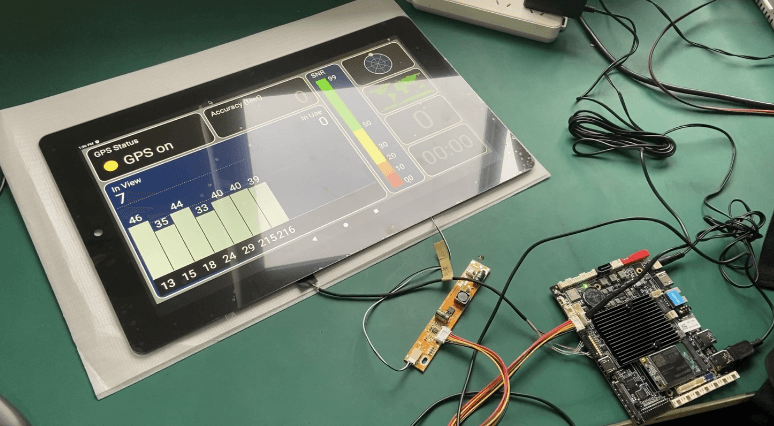
In the ever-evolving world of electronic devices, the integration between the TFT LCD display and the host device’s motherboard is a crucial aspect that often goes unnoticed.
As TFT LCD displays offer a diverse range of connectivity options, understanding how these interfaces connect to the motherboard is essential for a seamless visual experience.
In this article, we will explore the different connection methods and explore how the TFT LCD display interfaces integrate with the corresponding motherboard interfaces.
Interface definition matching
TFT LCD displays and motherboards may adopt different standardized video interfaces, such as HDMI, DVI, VGA, DisplayPort, LVDS, etc.
These interfaces differ significantly in pin definitions, signal types, and transmission characteristics.
If the interface definitions cannot be correctly matched, it will be difficult to achieve reliable connection between the two devices.
Taking the HDMI and VGA interfaces as examples, the former uses digital signal transmission with pin definitions including audio, video, clock, and other multiple signals; while the latter uses analog RGB signals with relatively fewer pins. If using a VGA cable to connect an HDMI interface, it is likely to cause signal distortion or inability to display normally.
Signal characteristic matching
In addition to the differences in interface definitions, the matching of signal characteristics is also a critical issue.
Different video interface standards may use different voltage levels, timing characteristics, and signal encoding methods.
For example, analog RGB signals and digital LVDS signals have vastly different transmission mechanisms.
If the correct signal conversion cannot be performed, it will be difficult to ensure the integrity and stability of the image.
To solve these problems, manufacturers often provide dedicated connection cables.
Such cables precisely match the interface of the TFT LCD display on one end and correspond to the video interface of the motherboard on the other end.
The quality of the connection cable itself is also crucial, as good shielding performance and conductivity can ensure signal integrity and avoid interference and attenuation.
Application of universal standard interfaces
In addition to using dedicated connection cables, another solution is to adopt universal standard video interfaces, such as HDMI or DisplayPort.
These interfaces are widely used in mainstream electronic devices, with strong compatibility, making it easier to find compatible connection cables.
Moreover, these interfaces usually support mechanisms like EDID, which can automatically identify devices and perform appropriate signal configuration, further simplifying the connection process.
However, even when using universal standard interfaces, some details still need attention.
For example, different generations of HDMI standards have differences in supported resolutions, color depths, HDR, and other features. If the HDMI versions of the motherboard and TFT LCD display do not match, compatibility issues may still arise.
Other solutions
For some professional applications, it may be necessary to use converters or video distributors as auxiliary devices to perform more complex signal conversion and distribution, in order to meet special connection requirements.
Conclusion
In short, the matching of the connection cable between the TFT LCD display and the motherboard is a difficult point that needs to be handled carefully.
Fully understanding the definition and signal characteristics of the interface between the two devices and choosing the appropriate dedicated connection cable or adapter are the keys to ensuring a reliable connection.
Only by solving this challenge can the seamless integration between the TFT LCD display and the motherboard be ensured.

