If you are designing a display solution, you may have to choose between LCD or OLED as your display type. LCD and OLED have different advantages and disadvantages, and you need to consider these when selecting the appropriate product for your specific application.
Related: What is OLED?
What is the Basic Principle of LCD and OLED?
The basic principle of LCD
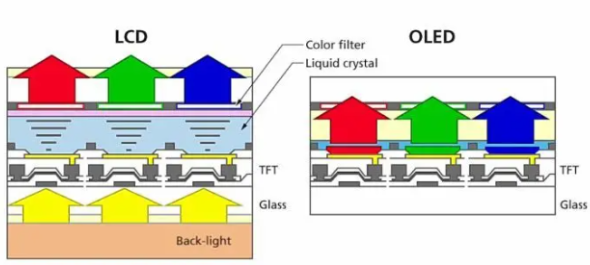
The principle of the LCDs is to place the liquid crystal between two pcs of conductive glass, driven by the electric field between the two electrodes.
This can cause the electric field effect of the liquid crystal molecules to twist and nematic, to control the transmission or shielding function of the light source and display images by generating light and dark between power on and off.
If add a color filter, a color image will be displayed.
The basic principle of OLED
OLED is a panel composed of organic light-emitting diode devices, also known as organic light-emitting semiconductors.
It uses a very thin coating of organic materials and a glass substrate.
When an electric current passes through, these organic materials will directly emit light.
The higher the current, the more luminous it is, so OLED displays do not require backlighting.
Divided by driving method, can be divided into PMOLED (passive driving type) and AMOLED (active driving type).
Related: PMOLED vs. AMOLED: What is the difference between?
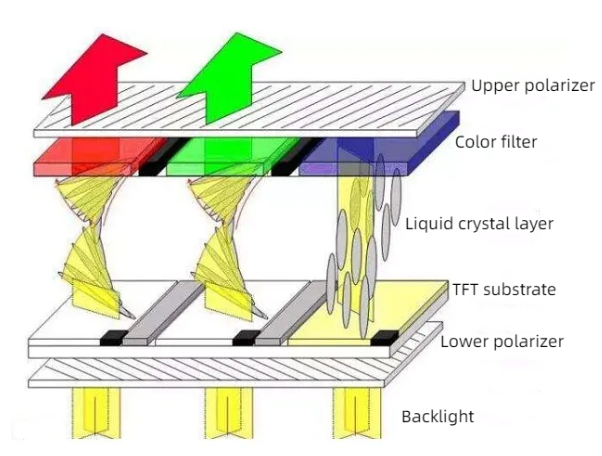
The Structure of LCD
TFT-LCD consists of an upper and lower substrate component, liquid crystal, a driver circuit unit, a backlight module, and other accessories.
Among them, the lower substrate component mainly includes the lower glass substrate and TFT array.
While the upper substrate component is composed of an upper glass substrate, a polarizing plate, and a membrane structure covering the upper glass substrate.
Liquid crystals are filled in the gaps formed by the upper and lower substrates.
If the LCD is colored, there are three primary colors (red, green, blue) filter units and black dots (black matrix) between the common conductive board and the glass substrate.
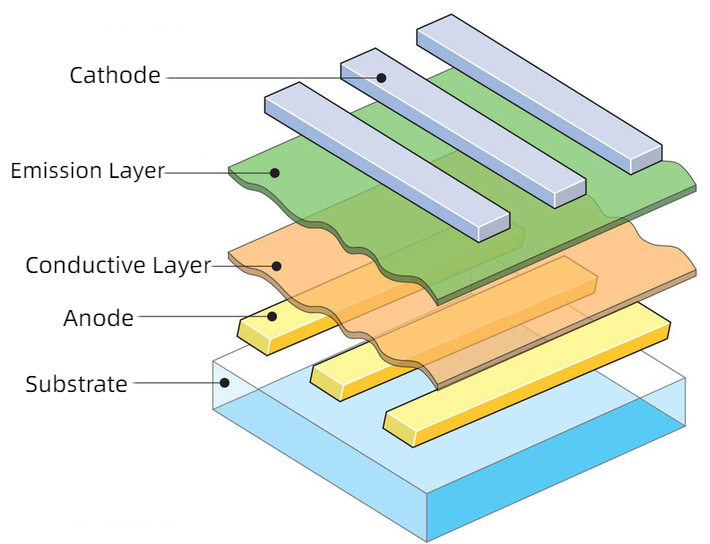
The Structure of OLED
The basic structure of an OLED is a thin, transparent, and semiconducting indium tin oxide (ITO), which is connected to the positive electrode of electricity, plus another metal cathode, wrapped into a sandwich structure.
The entire structural layer includes the hole transport layer (HTL), luminescent layer (EL), and electron transport layer (ETL).
LCD vs OLED: What is the Difference in features?
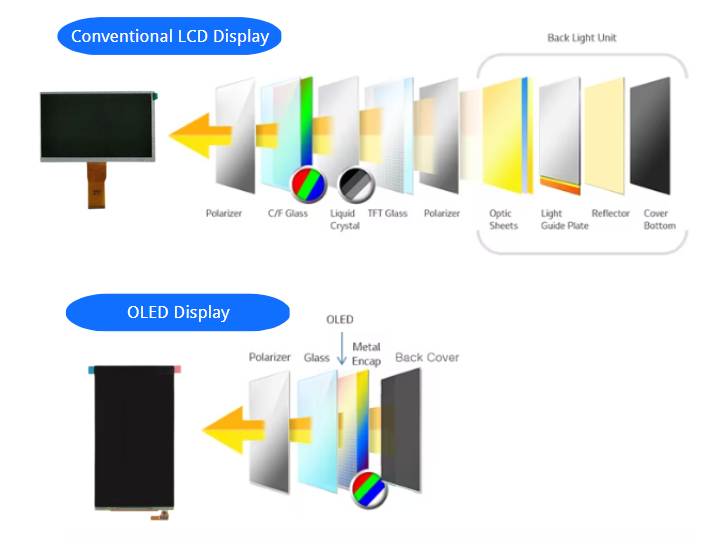
LCD and OLED have their advantages and disadvantages, and their differences are mainly manifested in the following seven aspects:
- Response speed
- Contrast ratio
- Viewing angle
- Power consumption
- Life span
- Price
LCD vs OLED: faster response time
Ordinary LCD TVs may experience delays (ghost images) because of the low response speed, resulting in significant differences in the screen when displaying images.
Generally, the response time of LCDs is 10ms, while that of OLEDs can reach 0.001ms.
Whether watching movies on OLED TVs or OLED phones, there will be no ghost images and better synchronization of sound and image can be achieved, providing consumers with a better experience.
LCD vs OLED: higher contrast ratio
Contrast refers to the ratio of white to black.
The higher the contrast, the stronger and clearer the image color.
Due to the backlight layer on the LCD, black is not pure black, making it difficult to increase the contrast.
While OLED is self-emitting without a backlight and has higher contrast. It can directly turn off some pixels in the black area, which is infinitely close to black.
As we mentioned in the previous section, OLED displays do not have a backlight. This means that OLEDs are much thinner than LCDs, and their pixels are closer to the surface of the monitor, giving them a wider viewing angle.
The OLED viewing angle can be up to 170⁰, but the most common type of LCDs don’t.
Based on LCD panel material, it can be divided into TN panels, VA panels, and IPS panels. The best viewing angle is the IPS panel, which can reach a viewing angle of 170⁰, while others are below 170⁰
Related: TN vs. IPS vs. VA: What’s the Best LCD Display Technology?
LCD vs OLED: lower power consumption
When LCD works, the entire backlight layer is turned on, while in OLED each pixel is independent and can light up certain pixels separately, which can greatly reduce the number of times the screen is lit.
This means that in normal use, OLEDs save more power than LCDs.
LCD vs OLED: lower life span
Due to OLED being an organic material, its aging rate is much faster than that of LCD, resulting in screen burning and a shorter lifespan.
According to data surveys, the average working time of the LCDs is approximately 60000 hours (2500) days.
However OLEDs are a new technology in the display market, and current OLEDs are expected to operate for 100000 hours with appropriate maintenance.
LCD vs OLED: higher production cost
Nowadays, LCD technology has developed very maturely, and the manufacturing cost of products has been decreasing year by year.
OLED technology is still in the developing stage, with complex manufacturing processes, increasing manufacturing maturity, and high product costs.
Currently, LCDs are still the mainstream in the market, and OLEDs have limited the penetration of OLED TVs, OLED phones, and other products due to high costs, fast aging, and low yield.
Conclusion
All in all, LCD and OLED both have their advantages.
In terms of solution selection, if you are sensitive to light, do not have high requirements for pure black color, and have a limited budget, LCD is may suitable for you.
If you are not sensitive to light, pursue the fashion and artistic sense of the product, have no economic pressure, and only want to try new high-tech, then OLEDs may meet your needs.
There are a lot of factors to consider when deciding on a display type for you, so we hope this guide makes your choice easier.
If you still have questions, feel free to contact our support center to talk to one of our engineers.

