Definition of OLED
An organic light-emitting diode (OLED), is also known as an organic electroluminescent (organic EL) diode.
It is a light-emitting diode (LED) in which the emissive electroluminescent layer is a film of organic compound that emits light in response to an electric current.
OLED is a current type of organic light-emitting device that emits light through the injection and recombination of carriers.
The light emission intensity is proportional to the injected current.
According to the driving method, OLED displays technology can be divided into the passive matrix (PM-OLED) and active matrix (AM-OLED).
Related: What is the difference between PMOLED and AMOLED?
Characteristics of OLED
- Low power consumption
Compared with LCD, OLED does not need a backlight, and the backlight is a relatively energy-consuming part of LCD.
- Fast response time
It can reach the microsecond level.
According to relevant data analysis, its response speed has reached about 1000 times that of LCDs.
- Wide viewing angle
It is actively emitting light, so the image will not display distortion within a large viewing angle range.
The viewing angle width from top to bottom, left to right, exceeds 170 degrees.
- High-resolution display
Most high-resolution OLED displays use AMOLED.
Its light-emitting layer can absorb 260,000 true-color high-resolution, and with the development of science and technology, its resolution will be higher in the future.
- Wide temperature
According to relevant technical analysis, it can operate normally at a temperature of -40℃~80℃.
In this way, geographical restrictions can be reduced, and it can be used normally in extremely cold regions.
- Soft screen
OLED can be produced on different flexible substrate materials such as plastics and resins, and a soft screen can be realized by evaporating or coating the organic layer on the plastic substrate.
- Lightweight
OLED has a relatively small mass and thickness compared to LCD.
Its seismic coefficient is higher and it can adapt to harsh environments such as high acceleration and vibration.
Application of OLEDs
It can be extended to the industries of electronic products, commerce, transportation, industrial control, and medicine.
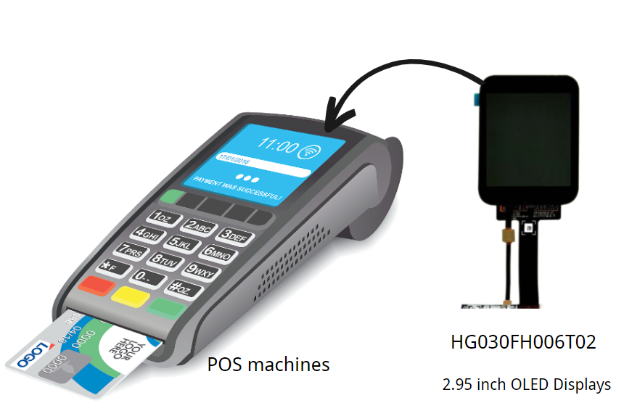
- Commercial industry
Small-sized OLED screens can be installed in POS machines, copiers, and ATMs.
Because OLED screens are bendable, thin, and strong in anti-aging performance, they are both beautiful and practical.

- Electronic products industry
Because the colors of OLED display screens are more vivid, and the colors can be adjusted (different display modes), it is widely used in practical applications.

- Transportation industry
It is mainly used for ships, aircraft instruments, GPS, videophones, vehicle displays, etc.,

- Medical industry
The impact of medical diagnosis and surgical screen monitoring are inseparable from the screen.
Conclusion
OLED displays have high development potential and great market potential, but compared to LCDs, OLED manufacturing technology is not yet mature enough.
Due to the disadvantages of low mass production rate and high cost, only high-end devices will use OLED displays in the market.
According to data from the first half of 2017, many manufacturers have increased their research investment in OLED technology, and many mid-range electronic products in China have applied OLED displays.
From the perspective of the mobile phone industry, the application proportion of OLEDs has been increasing year by year since 2015.
Therefore, the development of electronic products such as smartphones is bound to further promote the development of OLEDs.

