Thin-film transistor liquid crystal displays (TFT LCDs) are widely used in various electronic devices, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, televisions, and more.
In this article, we will explore the basics of TFT LCDs, including their sizes, resolutions, interfaces, contrast ratios, power consumption, refresh rates, viewing angles, aspect ratios, and more.
Sizes
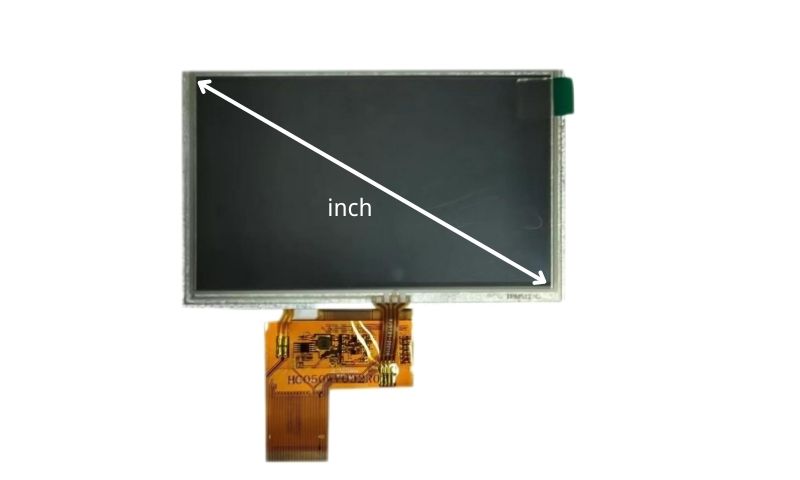
TFT LCDs come in a wide range of sizes, from small displays used in handheld devices to large displays used in televisions and digital signage.
The size of a TFT LCD is typically measured diagonally from one corner to another and is expressed in inches or centimeters.
Typical sizes for TFT LCDs include 7 inches, 10.1 inches, 15.6 inches, 24 inches, and 55 inches.
Resolutions
The resolution of a TFT LCD refers to the number of pixels that make up the display.
A pixel is the smallest unit of a digital image, and the more pixels a TFT LCD has, the sharper and more detailed the image will be.
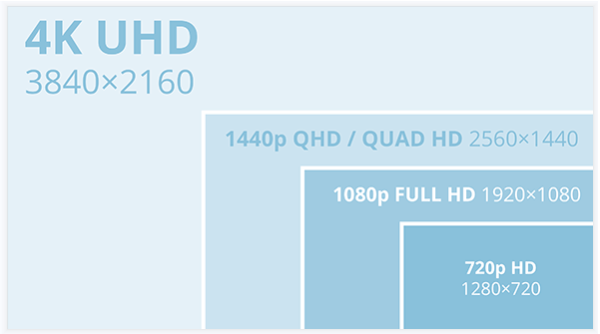
The resolution of a TFT LCD is typically expressed as the number of pixels in width by the number of pixels in height.
For example, a display with a resolution of 1920 x 1080 has 1920 pixels in width and 1080 pixels in height.
Common resolutions for TFT LCDs include 1366 x 768, 1920 x 1080, and 3840 x 2160.
Interfaces
TFT LCDs use a variety of interfaces to connect to devices, including LVDS, DVI, HDMI, VGA, MIPI, and eDP.
These interfaces allow devices to send video signals to the display, which then converts the signals into a visible image.
The choice of interface depends on the device and the display, and compatibility between the two is important for proper functionality.
Contrast Ratio
The contrast ratio of a TFT LCD refers to the difference between the brightest and darkest parts of the image.
A higher contrast ratio means that the image will have greater detail and depth, with darker blacks and brighter whites.
The contrast ratio is typically expressed as a ratio, such as 1000:1 or 3000:1, where the first number represents the brightness of the brightest part of the image and the second number represents the brightness of the darkest part of the image.

Power Consumption
TFT LCDs consume power to operate, and their power consumption can vary depending on size, brightness, and other factors.
Power consumption is typically measured in watts (W) or milliwatts (mW), and can be an important consideration for devices that run on battery power.
TFT LCDs can have different power consumption rates depending on whether they are in use or standby mode, and some displays may have energy-saving features to reduce their power consumption.
Refresh Rate
The refresh rate of a TFT LCD refers to the number of times per second that the image is updated on the screen.
A higher refresh rate means that the image will appear smoother and more fluid, especially when displaying fast-moving content such as video games or sports.
Refresh rate is typically measured in hertz (Hz), and common refresh rates for TFT LCDs include 60 Hz, 120 Hz, and 240 Hz.
Viewing Angle
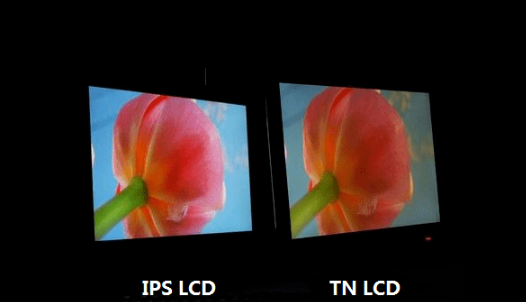
The viewing angle of a TFT LCD refers to the range of angles from which the image can be viewed without significant color distortion or loss of brightness.
A wide viewing angle means that the image can be viewed from more angles, making the display more versatile and user-friendly.
The viewing angle is typically expressed as the angle at which the image can be viewed without significant degradation, such as 178 degrees.
Aspect Ratio
The aspect ratio of a TFT LCD refers to the ratio of the width to the height of the display.
Common aspect ratios for TFT LCDs include 16:9, 16:10, and 4:3.
The choice of aspect ratio depends on the intended use of the display and can affect how content is displayed on the screen.
Response Time
The response time of a TFT LCD is the time it takes for a pixel to transition from one state to another.
A shorter response time means that the display can display fast-moving content more accurately and without visible artifacts.
Response time is typically measured in milliseconds (ms), and common response times for TFT LCDs include 1 ms, 4 ms, and 8 ms.
Conclusion
TFT LCDs are a fundamental technology used in a wide range of electronic devices, providing clear and sharp images for a variety of applications.
Understanding the basics of TFT LCDs, including their sizes, resolutions, interfaces, contrast ratios, power consumption, refresh rates, viewing angles, aspect ratios, and response times, can help users make informed decisions when selecting a display.
With continued advancements in technology and manufacturing, TFT LCDs will continue to improve and evolve, providing even better image quality and versatility in the future.

